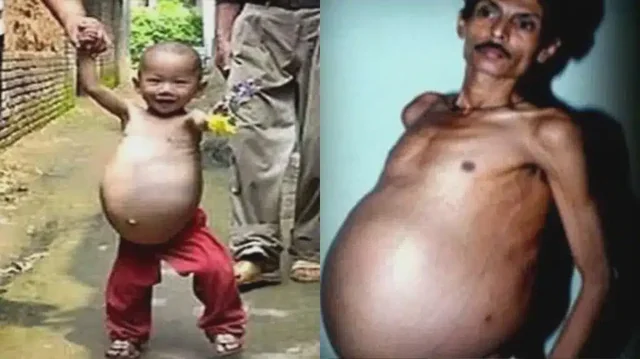
The human body is full of mysteries, but few are as astonishing as the case of a man who discovered he had been living with his twin inside him. This rare and perplexing condition, known as fetus in fetu, has fascinated medical experts and the general public alike. It challenges our understanding of human development, medical anomalies, and the human body’s resilience.
What is Fetus in Fetu?
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare developmental abnormality in which a fetus becomes enveloped by its twin during early pregnancy. Instead of developing as a separate individual, the twin becomes trapped inside its sibling’s body, surviving as a parasitic entity. While some medical experts classify FIF as an extreme form of teratoma (a type of tumor that can contain bone, hair, and teeth), others believe it is a separate phenomenon altogether.
The Discovery: A Shocking Revelation
In many documented cases, people live with their undeveloped twin for years without knowing it. Symptoms often emerge later in life, usually when the parasitic twin begins to grow, causing discomfort, pain, or unexplained swelling.
One such case involved a man who sought medical attention due to persistent abdominal pain and bloating. After undergoing imaging scans, doctors were stunned to find what appeared to be a mass containing bones, hair, and even partially developed organs. Further analysis revealed that this mass was, in fact, his twin—his biological sibling that had never fully developed outside his body.
Medical Examinations and Diagnosis
The diagnosis of fetus in fetu is confirmed through a combination of imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds. These scans typically reveal:
A mass with vertebral structures, suggesting a fetal form.
Limbs, hair, and even rudimentary organ development.
An encapsulated structure with its blood supply, though usually non-functional.
Biopsies and surgical exploration further confirm whether the mass is genuinely a parasitic twin or a complex tumor.
How Does Fetus in Fetu Occur?
Fetus in fetu occurs due to an abnormality in monozygotic twin development. When an embryo splits to form identical twins, one twin sometimes becomes enveloped within the other due to a failure of proper separation. Over time, the enveloped twin remains suspended, neither growing into a whole person nor entirely disappearing. It may continue to develop minimally, deriving nutrients from the host twin but never becoming independent.
The Difference Between Fetus in Fetu and Teratomas
One of the biggest debates in medical science is whether FIF is genuinely distinct from teratomas. The key differences include:
Fetus in Fetu typically exhibits an organized fetal structure, often with a recognizable spine and limbs.
Teratomas are tumors that contain a chaotic mixture of tissues but lack a structured form.
FIF often contains tissue derived from all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), further supporting the argument that it is a developmental twin rather than a tumor.
Documented Cases of Fetus in Fetu
Cases of fetus in fetu have been recorded worldwide, with fewer than 200 cases ever documented. Some notable instances include:
The Indian Infant Case (2003): A baby boy in India was diagnosed with FIF after doctors noticed a lump in his stomach. Surgery revealed his twin inside him, with identifiable limbs and a partially formed head.
The Indonesian Man (2017): A 36-year-old man had suffered from chronic pain for years before a medical scan revealed that he was carrying his twin in his abdomen.
A Chinese Teenager (2015): A 15-year-old boy experienced severe stomach pain, only to discover that he had been carrying his twin brother inside him since birth.
The Surgical Removal Process
Treatment for fetus in fetu involves surgical removal, which can be complex depending on the location and attachment of the parasitic twin. The procedure includes:
Pre-Surgical Imaging: To determine the parasitic twin’s structure, size, and attachment points.
Careful Extraction: Surgeons must meticulously separate the twin from surrounding tissues to prevent damage to the host patient’s organs.
Post-Operative Care: Recovery typically involves monitoring for infections and ensuring the patient’s body adapts after removing the mass.
Psychological and Ethical Considerations
Beyond the medical aspects, discovering that one has been carrying their twin inside them raises deep psychological and ethical questions. Some patients experience emotional distress upon learning they had a twin that never fully developed.
Ethically, the debate arises over whether the parasitic twin should be classified as a separate individual or merely a biological anomaly. While medical experts see FIF as a medical condition rather than a lost life, cultural and personal beliefs sometimes complicate this perspective.
Could the Twin Have Been Alive?
While the parasitic twin may contain bones, hair, and even rudimentary organs, it is not a living, conscious being. In most cases, FIF does not develop a brain or a functioning nervous system, meaning it cannot think, feel, or exist independently. It is merely a collection of tissues that stopped developing at an early embryonic stage.
Conclusion
The case of a man with his twin living inside him is a rare yet fascinating example of the complexities of human development. Fetus in fetu remains one of the most unusual medical conditions ever documented, reminding us of the intricacies of life, the potential for extraordinary anomalies, and the incredible adaptability of the human body. Though rare, FIF intrigues doctors, scientists, and the general public, offering a glimpse into the mysteries hidden within us all.